Brief "Terminology of Terminology"
To make it easier for you to work with quickTerm, it would be helpful to briefly explain the entry structure concept used in MultiTerm. This is generally accepted in terminology theory and is referred to as being "concept-oriented and term-independent". This means that terms, which represent the same concept, are contained within the same entry using the same ID. Homonyms - terms which by coincidence have the same working but mean something totally different (e.g. button on clothes vs. button on a GUI) are not stored in the same entry.
It is important to familiarize yourself with the notion of "concept", "language" and "term" if you want to be able to filter entries or terms and also understand approval and translation workflows.
Concept
An entry in terminology always depicts a certain "thing" or "feature", independent of the actually linguistic representation (term). This "thing" can be described independently of any terms or even language. In the terminology, this abstract "thing" is referred to as a "concept".
Language
Different designations can exist in different languages for each concept. Not all languages are not available all the time.
Term
If the designations are in written form (i.e., they are "words"), they are referred to in the terminology used as "terms". If there are multiple terms associated with a language in an entry, these are also referred to as synonyms. For example, chair and seat could be synonyms.
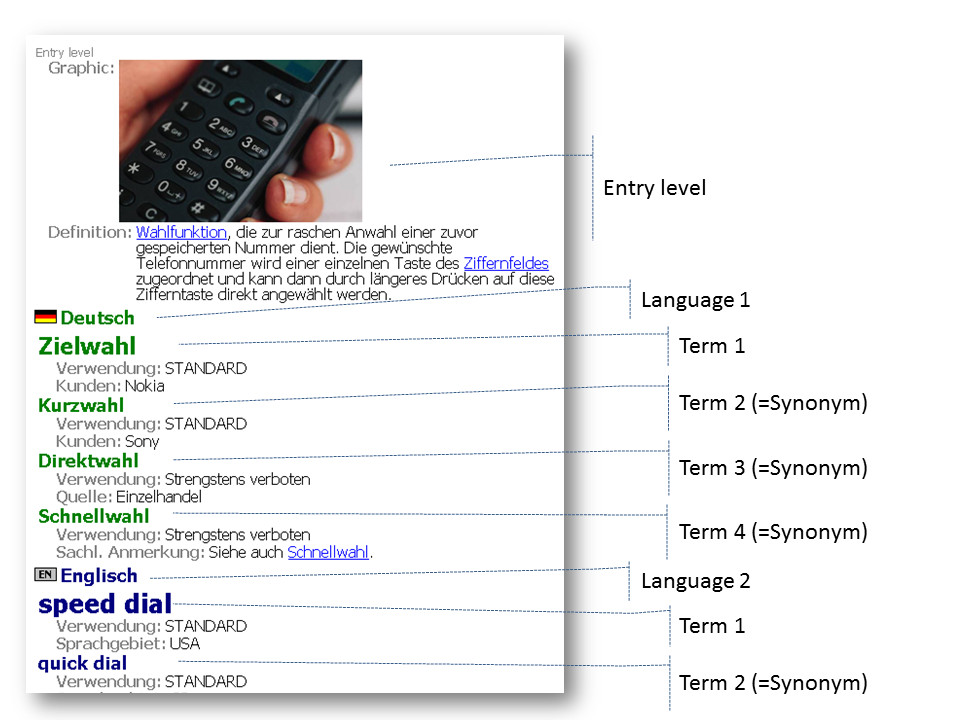
An example
MultiTerm Entry Structure
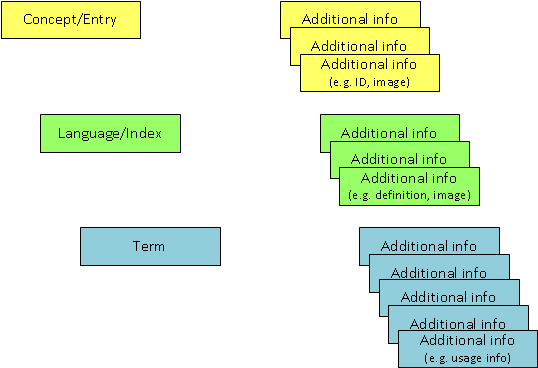
As you can see, a MultiTerm entry has three levels:
- ▪
- a concept level, on which can be found all the information that is always valid for the concept (=the "thing") in every language.
- ▪
- One or more language levels
- ▪
- one or more terms (term level)
- Additional information can be entered for each term, so as to be able to distinguish more clearly between the terms and, in particular, to clarify the differences in use.
Schematic Entry Structure